Electric cars are increasingly popular among environmentally conscious consumers.
They offer reduced emissions and lower fuel costs.
One common query is whether low amperage can damage the car battery.
Yes, low amperage can potentially damage an electric car battery by causing sulfation, reducing capacity, and shortening lifespan.
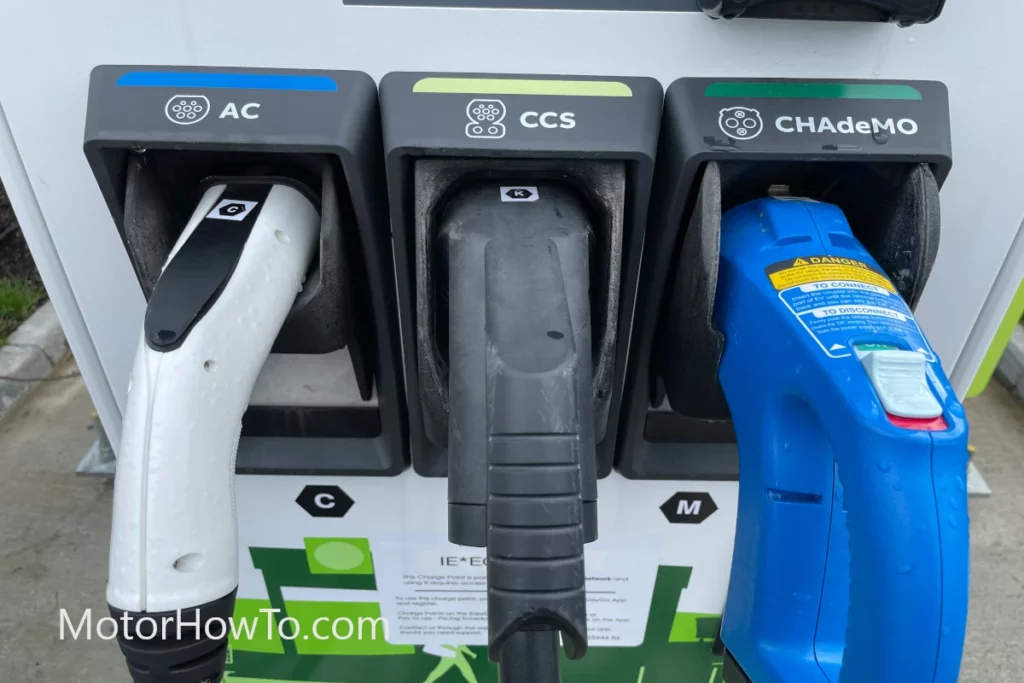

Car batteries are essential to electric cars, powering the motor and other systems.
Any damage to the battery can result in decreased performance and increased maintenance costs.
Low amperage is a term used to describe a low current flow in an electrical circuit and has been suggested to harm an electric car battery.
This article will explore the relationship between low amperage and car battery damage.
Related:
- How Hot Does An Electric Car Battery Get? (Read First)
- How Long Can An Electric Car Sit Without Being Driven? (Explained)
- What Happens When Electric Vehicle Loses Power? (Must Read)
How Does Amperage Affect Car Battery?
The amperage can significantly impact the health and longevity of a car battery. A low amperage flow is generally considered safe and beneficial when a battery is being charged.
This is because the charging process helps to break down any sulfation that may have occurred in the battery, a natural process that can reduce the battery’s capacity over time.
A low amperage charge can help to prevent and reverse sulfation, prolonging the battery’s life. On the other hand, a high amperage flow can harm the battery, particularly during the charging process.
High amperage charging can generate excess heat, damaging the battery’s internal components and shortening its lifespan.
A high amperage flow can cause the battery to overheat and potentially catch fire, presenting a safety hazard. In the case of an electric car battery, a low amperage flow is generally safe.
You may need a higher amperage flow for faster charging times, but this should always be done under the manufacturer’s recommendations to avoid damaging the battery.
Overall, proper charging and maintenance of the car battery, including monitoring the amperage flow, can help to maximize its lifespan and ensure optimal performance.
How Many Amps Will Drain A Car Battery?
The number of amps that can drain a car battery depends on various factors, such as the battery’s capacity, age, condition, and the amount of time the battery is being used.
In general, it is recommended to avoid draining a car battery below 50% of its capacity is recommended, as doing so can shorten the battery’s lifespan.
A fully charged car battery should be able to power the car’s lights, radio, and other accessories for several hours without being recharged.
The average car battery has a capacity of around 48-50 amp-hours. However, this capacity can vary depending on the battery’s age and condition.
As a general rule, it is recommended not to use more than 25% of the battery’s capacity at any given time, as this can help to prolong the battery’s life. For example, you should not use a 48 amp-hour battery for more than 12 hours without recharging.
It is also important to note that certain electrical devices, such as car alarms, can draw power from the battery even when the car is turned off, which can cause the battery to drain more quickly.
Overall, it is important to be mindful of the amount of power being drawn from the car battery and to avoid draining it below 50% of its capacity. Regular maintenance and charging can help to prolong the battery’s lifespan and ensure optimal performance.
What Voltage Is Too Low To Charge A EV Battery?
The voltage at which an electric vehicle (EV) battery is considered too low to charge depends on the specific battery chemistry and design. Most modern EV batteries are lithium-ion, and the minimum voltage required for charging can vary depending on the state of charge and temperature of the battery.
Generally, a lithium-ion EV battery should not be charged when the voltage is below 2.5 volts per cell, or approximately 30% charge.
Charging a lithium-ion battery at a voltage lower than this can cause damage to the battery’s internal components and reduce its lifespan.
It is also important to avoid fully discharging a lithium-ion EV battery, as this can cause irreversible damage and significantly reduce capacity.
EV battery management systems are designed to monitor and maintain the appropriate voltage levels during charging to prevent damage to the battery.
These systems can adjust the charging voltage based on the state of charge, temperature, and other factors to ensure safe and efficient charging.
Following the manufacturer’s recommendations for charging and maintaining the EV battery is important to ensure its longevity and optimal performance. Regular monitoring of the battery’s state of charge and voltage can also help to detect any potential issues and prevent damage to the battery.
What Happens If You Charge A Battery With More Amps?
If an electric vehicle (EV) battery is charged with too many amps, it can result in overcharging and overheating of the battery, which can cause damage and reduce its lifespan.
Overcharging can cause the electrolyte solution inside the battery to evaporate, leading to a loss of capacity and performance.
Overheating can also cause the battery’s internal components to degrade and increase the risk of a thermal runaway event, leading to a fire or explosion.
Most EV batteries are equipped with battery management systems (BMS) that regulate the charging process and monitor the battery’s state of charge and temperature to prevent overcharging and overheating.
The BMS can adjust the charging rate based on these factors to ensure safe and efficient charging. Most EV charging stations are designed to limit the charging rate to a safe and appropriate level for the specific battery.
It is important to note that charging an EV battery with more amps than it can handle can also damage the charging equipment, such as the charging cable or charging station. This can result in additional costs for repair or replacement.
Overall, it is essential to follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for charging the EV battery and use a charging station compatible with the specific battery. Avoiding overcharging and overheating can help to prolong the battery’s lifespan and ensure the safe and efficient operation of the EV.
Conclusion
Low amperage can cause damage to the battery of an electric car by reducing its capacity, shortening its lifespan, and causing sulfation.
On the other hand, a high amperage flow can also damage the battery by generating excess heat during the charging process.
To ensure optimal performance and maximum lifespan of a car battery, it is essential to charge and maintain it properly, monitoring the amperage flow to ensure it is within the manufacturer’s recommendations.
Regular maintenance and charging can help to prolong the battery’s lifespan and ensure optimal performance.
It is also important to note that the number of amps that can drain a car battery depends on various factors. It is recommended not to use more than 25% of the battery’s capacity at any given time to prolong its life.
Moreover, the voltage at which an EV battery is considered too low to charge depends on the specific battery chemistry and design.
Following the manufacturer’s recommendations for charging and maintaining the EV battery is essential to ensure its longevity and optimal performance.
Finally, it is crucial to avoid charging an EV battery with more amps than recommended, as this can result in overcharging and overheating the battery, causing damage and reducing its lifespan.
Sources
CHARGING 101: HOW DO AMPERAGE, VOLTAGE, AND WATTAGE AFFECT CHARGING DEVICES?
How Many Amps Should I Charge My Car Battery At?
Electric Car Damage from Battery Being Too Powerful?
What Do Amp Hours Actually Tell You About a Battery?



